Recently I was asigned with a task to implement downloading file from server to client machine using web browser. I've encountered on few specifics described below.
Basics
- Client side logic have to send HTTP GET request to remote server IP address with requesting file with a certain name.
- Server side logic should accept HTTP GET request and
- read file from local file system and put it in response body,
- set Content-Disposition HTTP header to attachment informing client how downloaded file should be treated.
- inform browser that it is allowed to read additional headers from response by setting Access-Control-Expose-Headers HTTP header or otherwise browser will not be able to read Content-Disposion and Content-Lenght headers due to browser inbuilt security.
Server side - Spring
Let's create Spring controller and one endpoint capable to accept client's HTTP GET request and serve the requested file.
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/files")
public class FileController {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@GetMapping("/{filename:.+}")
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity<Resource> serveFile(@PathVariable String filename) {
Resource file = applicationContext.getResource("file:C:/test/" + filename);
if (file.exists()) {
HttpHeaders headers=new HttpHeaders();
//instructing web browser how to treat downloaded file
headers.add(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION,"attachment; filename=\\\\"" + file.getFilename() + "\\\\"");
//allowing web browser to read additional headers from response
headers.add("Access-Control-Expose-Headers",HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION + "," + HttpHeaders.CONTENT_LENGTH);
//put headers and file within response body
return ResponseEntity.ok().headers(headers).body(file);
}
//in case requested file does not exists
return ResponseEntity.notFound().build();
}
}
Client side - React
Step 1
Supposing you've already created React project, now create service.jsx file to setup basic client HTTP connection parameters
import axios from 'axios';
class Service {
getRestClient() {
if (!this.serviceInstance) {
this.serviceInstance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://localhost:8080/',
timeout: 10000,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
});
}
return this.serviceInstance;
}
}
export default (new Service());
where
- baseURL is URL of server,
- timeout is max timeout interval for axios server instance to establish connection with server. If server cannot be reached and this interval expires, axios will throw Timeout error exception.
- header 'Content-Type': 'application/json' will be sent within request informing server that client expects json formatted answer.
Note that service is implemented using Singleton pattern. It means that Service object instance will be unique: constructed only once and later reused for all calls.
axios javascript library is probably all you'll ever need if you intend to send HTTP requests from your web page.
Step 2
Create file-service.jsx file using new service to setup Java Script Promise object for file download request
import service from './service.jsx';
export class FileService {
getFileFromServer(fileName){
//returns Promise object
return service.getRestClient().get('/files/'+fileName,{ responseType:"blob" });
}
}
Note that we additionally instructed axios client to expect response type blob.
Step 3
Lets create React component for file downloading
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { FileService } from '../services/file-service.jsx';
import { Button } from 'primereact/components/button/Button';
import { saveAs } from 'file-saver';
export class DownloadFile extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.fileService = new FileService();
this.state={downloading:false};
}
extractFileName = (contentDispositionValue) => {
var filename = "";
if (contentDispositionValue && contentDispositionValue.indexOf('attachment') !== -1) {
var filenameRegex = /filename[^;=\\
]*=((['"]).*?\\\\2|[^;\\
]*)/;
var matches = filenameRegex.exec(contentDispositionValue);
if (matches != null && matches[1]) {
filename = matches[1].replace(/['"]/g, '');
}
}
return filename;
}
downloadFile = () => {
this.setState({ downloading: true });
let self = this;
this.fileService.getFileFromServer("test.png").then((response) => {
console.log("Response", response);
this.setState({ downloading: false});
//extract file name from Content-Disposition header
var filename=this.extractFileName(response.headers['content-disposition']);
console.log("File name",filename);
//invoke 'Save As' dialog
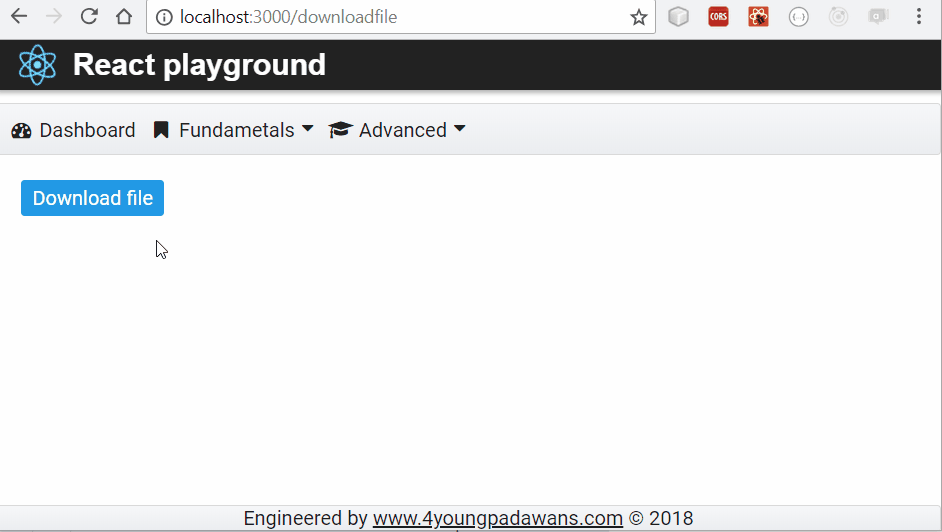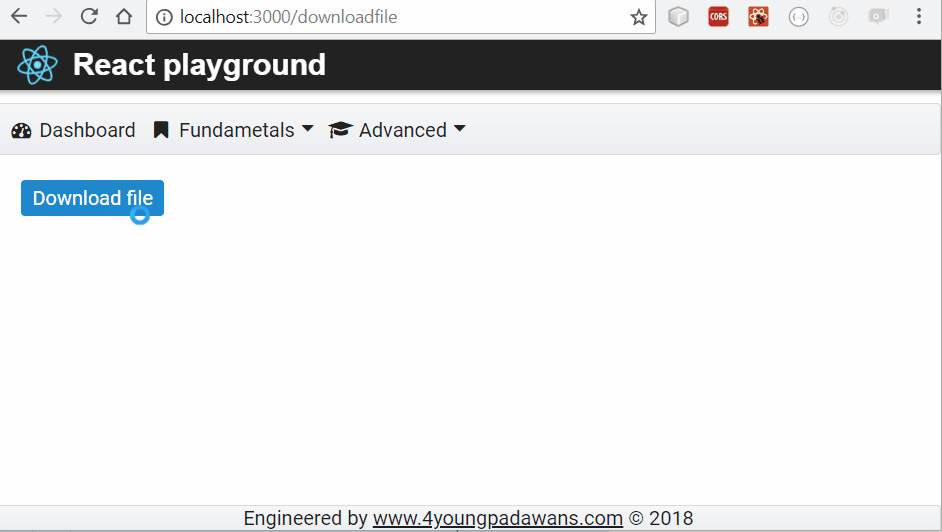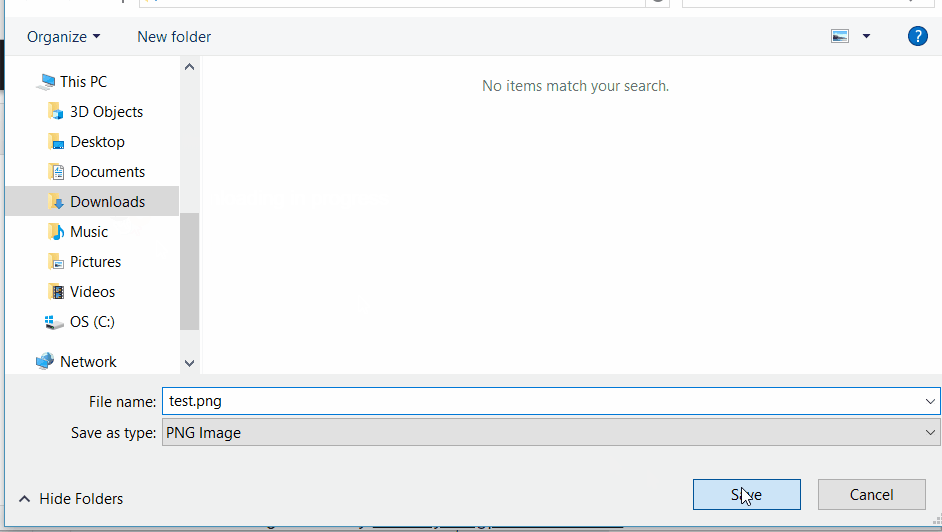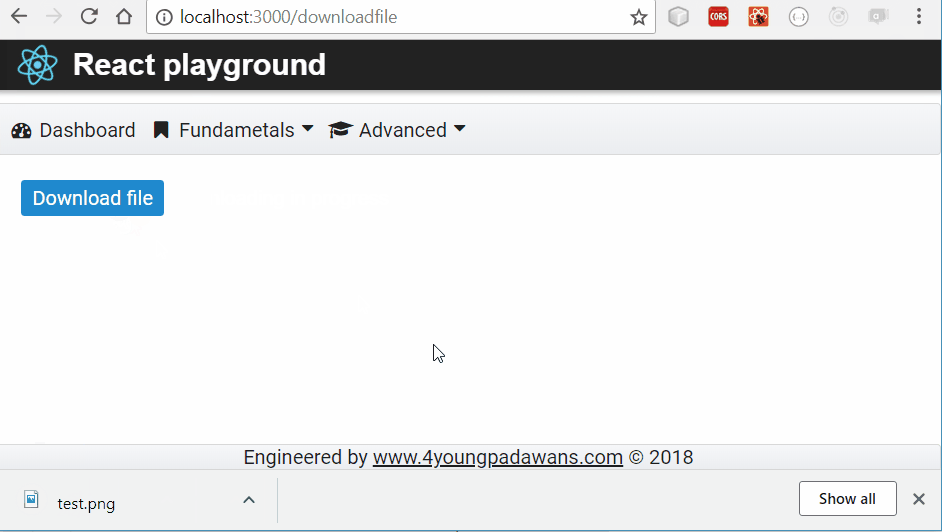
saveAs(response.data, filename);
}).catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
self.setState({ downloading: false });
if (error.response) {
console.log('Error', error.response.status);
} else {
console.log('Error', error.message);
}
});
};
render() {
console.log("state",this.state);
return (
<div>
<Button label="Download file" onClick={this.downloadFile} />
<label>{this.state.downloading ? 'Downloading in progress' : ''}</label>
</div>
)
};
}
In previous code we used file-saver package that has good cross-browser implemenation for file downloading.
Step 4
Now we only need to put new component inside React's top level component (App.js file)
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import {FileDownloader} from './components/fileDownloader.jsx';
export class App extends Component {
render(){
return (
<div>
<FileDownloader />
</div>
);
}
}
Result